

© Roman Kybus - istock.com
Hotmelts and reactive hotmelts in industry - A history of evolution
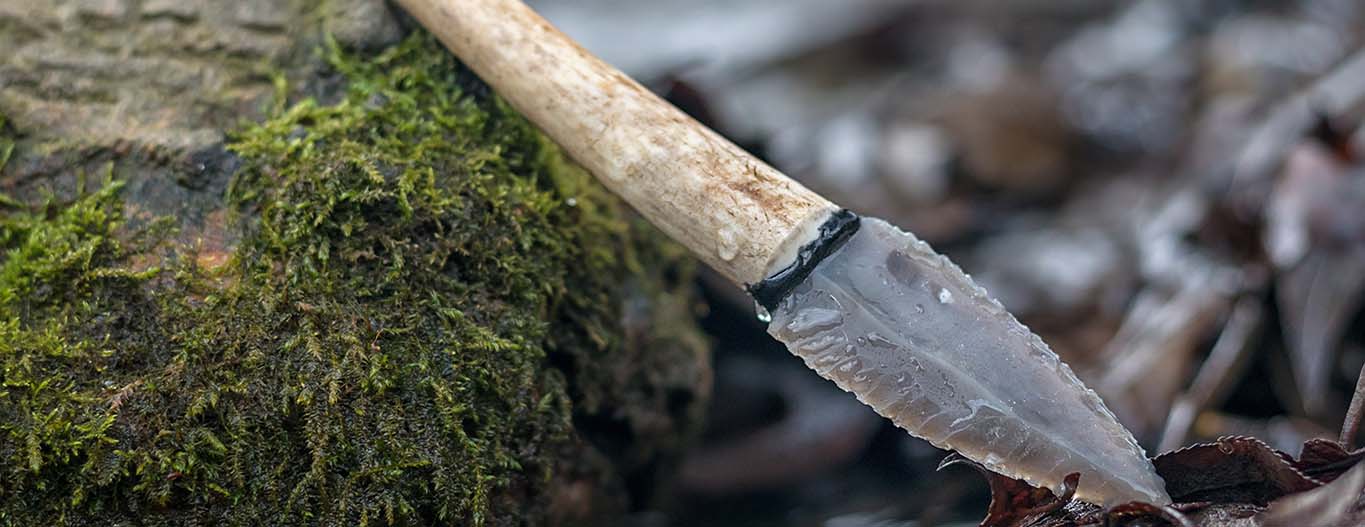
Unobstrusive but indispensable. Adhesives are probably as old as mankind itself is and have always been an irreplaceable part of our everyday lives. As early as the Stone Age, birch pitch was produced by dry distillation over a wood fire and used as an adhesive. Archaeologists were able to prove this during the excavation of a Stone Age weapons depot.
Nowadays, adhesives can be found in almost every everyday object. Like our everyday objects, the adhesives used in them are subject to constant evolution. This evolution has been massively accelerated in recent decades. Many new products and production processes have ensured that bonding as a joining technique has developed greatly. The adhesives market has increased rapidly over the last century. An enormous variety of different adhesive types has been developed.


© KLEIBERIT


© KLEIBERIT
Industrial adhesives must meet high standards,
The requirement profile of an industrial adhesive depends, for example, on the materials to be bonded. Plastics, wood and wood-based materials, metals and mineral materials are bonded together in countless applications. Depending on the purpose, an adhesive bond should have certain properties. Flexible, rigid, removable or permanently strong are typical requirements. Furthermore, long-lasting durability is important. Strong temperature fluctuations, chemicals, humidity, weathering or mechanical loads can stress an adhesive bond.
The requirements for the manufacturing process of a product and the associated economic efficiency also play a major role. Industrial adhesive systems are often processed in automated production processes. At the subsequent user, they are then brought to a processable state by means of special melting equipment and transported via suitable conveying units to the application units, such as a slot nozzle, spray nozzle or roller. The processing techniques in the adhesive processing industry are diverse. In most cases, the goal is always the same - high production speeds and a bond perfectly matched to the application.

© Bergringfoto - Fotolia


© KLEIBERIT


© in4mal - Fotolia


© Black Jack - Fotolia


© interiorphoto - Fotolia


© Cyprych Kalienke


© KLEIBERIT


© Cyprych Kalienke
Hotmelt and reactive hotmelt adhesives score for their high level of customizability
Every adhesive joint, including its production process, has its own specific requirements. Countless converting processes realize countless joining methods. In industry, hotmelt adhesives have proven to be particularly adaptable. Typical industrial sectors in which hotmelt adhesives are in use are listed below.
Non-reactive hotmelts are based on a thermoplastic base polymer. By adding synthetic resins, oils, or waxes, the adhesive can be formulated to meet exact individual requirements. Non-reactive hotmelts include EVA hotmelts, polyamide hotmelts, and polyolefin hotmelts.


© slavun - Fotolia
EVA hotmelts – adhesives based on ethylene vinyl acetate
Due to their excellent price-performance ratio and effective thermal stability, EVA hotmelts are widely used in industry,
for example in:
-
packaging
-
bookbinding
-
furniture making
Reactive hotmelt systems are technically advanced and extremely adaptable. They have several advantages over non-reactive adhesives. They harden by physical means as well as through a chemical reaction upon the uptake of air humidity or UV radiation. The adhesive bond becomes non-meltable after the chemical reaction, which positively affects the quality of the bonding. Bonds created with reactive PUR hotmelts are highly resistant to heat, cold, moisture, and mechanical stresses. The formulations can be adapted to individual requirements, leading to customized adhesives that meet very specific needs.
Reactive polyurethane hotmelts (PUR hotmelts)
Reactive polyurethane adhesives are used for very complex applications. These adhesives have seen huge developments in recent decades. With the right know-how, they can be used to achieve exceptional bond quality. Reactive PUR hotmelts have a huge resistance to external factors such as strongly fluctuating temperatures, constant mechanical loads, and chemicals.
Reactive PUR hotmelts achieve extremely strong adhesive bonds, perfectly coordinated across the production process.
Reactive hotmelts in micro-emission quality
Reduced-emission products are currently setting the trend in the field of reactive hotmelts. To meet the current REACH regulations aimed at improving the protection of human health and the environment from the risks posed by chemicals, the European Union resolved to make PUR adhesives even safer. Growing public interest for low-pollutant and more environmentally friendly products is also increasing the demand for reduced-emission PUR hotmelts. Their bonding quality and processing properties are practically identical to conventional reactive hotmelts. Additional benefits are:
-
environmentally friendly manufacturing process
-
no labeling obligation with P and H hazard statements
-
safe and easy handling
-
cost-effective equipment due to simplified extraction systems
-
identical bonding properties (to conventional methods)
Bio-based hotmelts
PUR adhesive systems based on sustainable, plant-based raw materials are becoming increasingly popular. However, it is important that only such plant-based raw materials that are not suitable for food production are used. Bio-based hotmelts achieve excellent bonding performance, comparable with conventional PUR hotmelts.

Gluing is the bonding technology of the future
Hotmelts have revolutionized joining technology in recent decades. Gluing continues to have a promising future, having multiple advantages over many other joining methods, and adhesive technologies are developing constantly to meet the growing variety of materials on the market. The results are glue joints that are tailored to the individual materials they are bonding and that can be realized in very economical production processes.
However, an adhesive is only as good as how it can be processed. Achieving the perfect bond therefore depends on the adhesive formulation and how and where the adhesive is used. KLEIBERIT’s engineers have decades of experience in this field and have created many efficient solutions for numerous industrial uses. Our expertise is valued worldwide. Renowned companies and machine manufacturers in the adhesive processing sector and other industries trust in KLEIBERIT's products and services. More information about the industrial uses of KLEIBERIT adhesives can be found here.
Source of information
www.klebstoff-presse.com/fileadmin/redaktion/ivk/Kuriose_Klebstoff-Fragen.pdf, 08.07.2021 www.welt.de/wissenschaft/article3718912/Zweikomponenten-Kleber-aus-der-Steinzeit.html, 08.07.2021 www.welt.de/wissenschaft/article7698868/Forscher-entdecken-Klebstoff-an-Steinzeitwaffen.html, 09.07.2021 de.wikipedia.org/wiki/Schmelzklebstoff, 09.07.2021 echa.europa.eu/de/regulations/reach/understanding-reach, 09.07.2021 Möbelfertigung: Ausgabe 3, 2019 – Ligna Spezial. „Sichere Produkte sind in Jedermanns Interesse“




